Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Presidential Plenary Session 2
9 - Rifaximin Monotherapy Is More Effective Than Lactulose Monotherapy for Reducing the Risk of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy (OHE) Recurrence and All-Cause Mortality: An Analysis of Two Randomized Trials
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:06 AM - 10:18 AM ET
Location: Terrace Ballroom

Jasmohan S. Bajaj, MD, MS, FACG
Professor
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine
Richmond, VA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Outstanding Research Award in the Liver Category
Jasmohan S.. Bajaj, MD1, Robert S.. Rahimi, MD2, Christopher Allen, MS3, Zeev Heimanson, PharmD3, Robert J.. Israel, MD3, Kris V.. Kowdley, MD, FACG4
1Virginia Commonwealth University and Central Virginia Veterans Healthcare System, Richmond, VA; 2Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 3Salix Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ; 4Liver Institute Northwest, Seattle, WA
Introduction: Lactulose (LAC) monotherapy (MT) is recommended as secondary prophylaxis after the first instance of OHE, with LAC plus rifaximin prescribed should additional OHE events occur. However, LAC nonadherence, which can precipitate OHE recurrence, indicates that alternative, non-LAC–based strategies are needed. The aim was to evaluate the efficacy/safety of LAC MT vs rifaximin MT.
Methods: Data were analyzed post hoc from 2 randomized trials (phase 3 double-blind; phase 4 open-label) of adults with cirrhosis and a history of OHE during the previous 6 months (currently in remission [Conn score ≤1]). Only patients who treated with rifaximin 550 mg twice daily (ie, no LAC [phase 3 or 4 trials]) or LAC (titrated to 2-3 soft stools/d) plus placebo (ie, LAC MT [phase 3 trial]) were included in the analysis. The primary efficacy endpoint was time to first breakthrough OHE episode (Conn score ≥2; original endpoint in both trials).
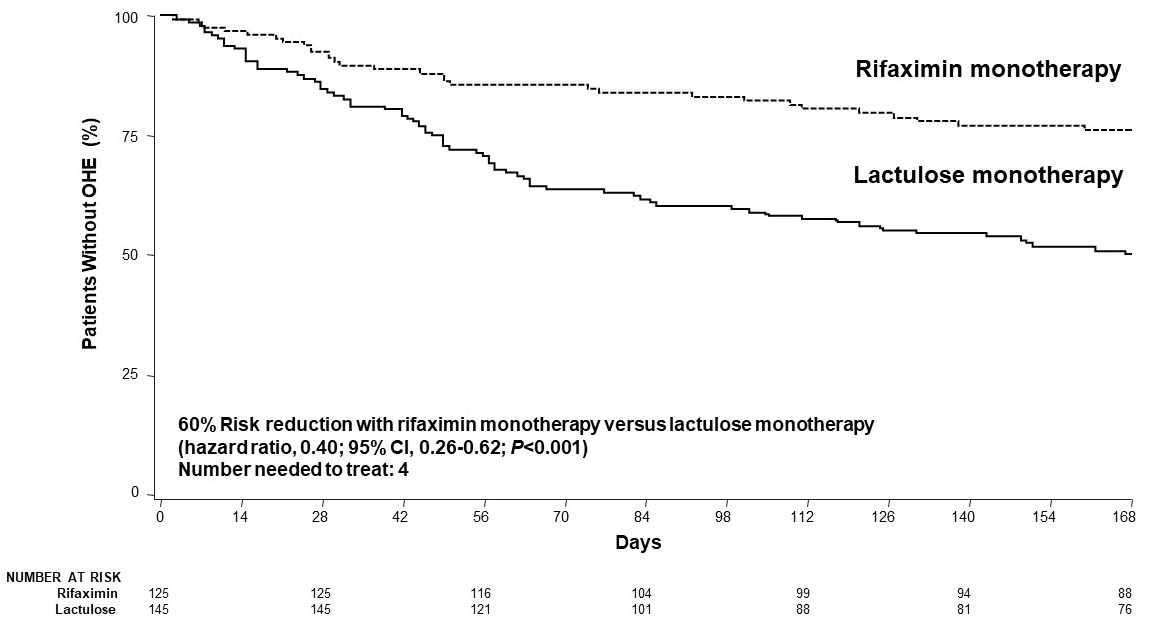
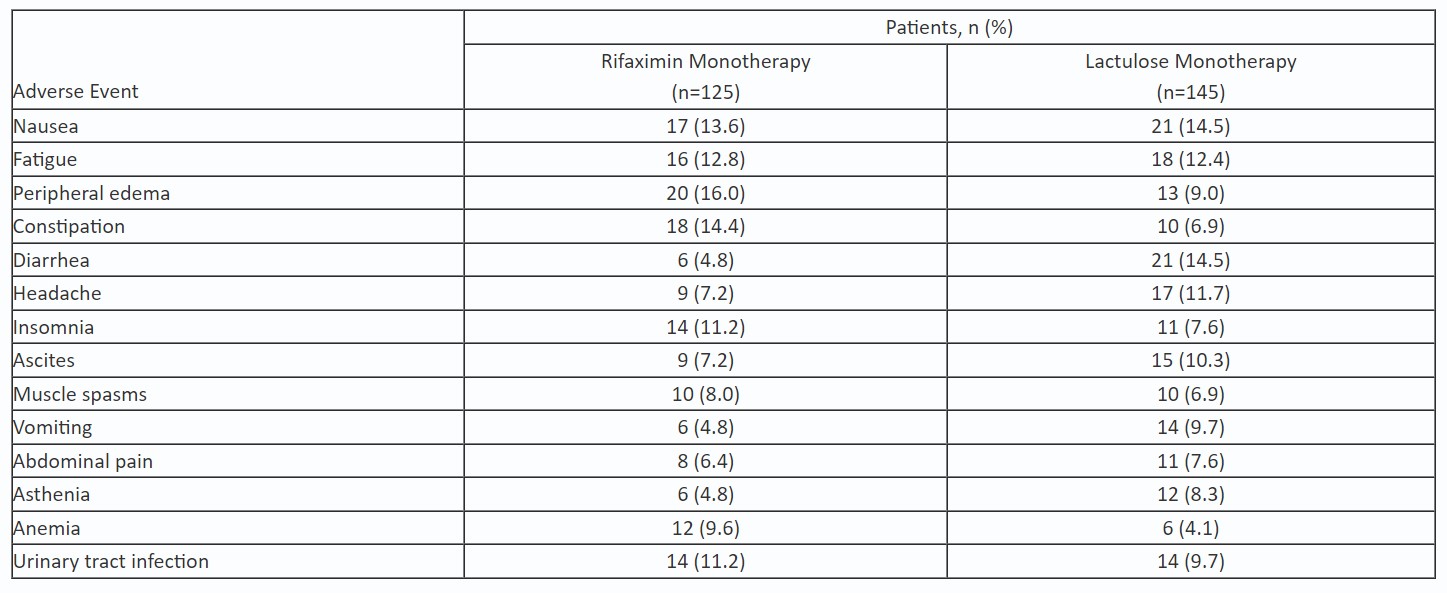
Results: 125 patients received rifaximin and 145 patients received LAC. The majority of patients (rifaximin; LAC) were male (60.0%; 68.3%), the mean age was about 57 y (58.2 y; 56.6 y), the median MELD score was 12 in both groups, and about half (51.2%; 46.2%) were Child-Pugh class B. A significantly smaller percentage of patients treated with rifaximin MT had an OHE episode vs those treated with LAC MT (23.2% vs 49.0%, respectively; P< 0.0001). Rifaximin MT reduced the risk of a breakthrough OHE episode by 60% vs LAC MT during 6 months of treatment, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 4 (Figure). There was a lower mortality rate in rifaximin MT vs lactulose MT group (1.6% vs 4.8%; P< 0.001), with a NNT of 19 (HR, 0.048; 95% CI, 0.01-0.29). Through follow-up (14±2 days posttreatment), mortality was reported for 2 (1.6%) patients in rifaximin MT and 10 (6.9%) patients in lactulose MT groups. Of patients who died during the study, 2 had baseline C-P class A (LAC group), 9 class B (rifaximin [n=2]; LAC [n=7]), and 1 class C (LAC group); only 2 patients (1 in each group) had a baseline MELD score of 19 or more. More LAC-treated vs rifaximin-treated patients discontinued early from study (62.1% vs 36.0%), most commonly due to HE recurrence. Rifaximin MT was well tolerated (Table).
Discussion: Significantly fewer OHE recurrence episodes were reported with rifaximin MT compared with LAC MT in patients with a history of OHE. In addition, rifaximin treatment may confer a survival benefit. Rifaximin MT may be an appropriate management approach in select patient populations.
Disclosures:
Jasmohan S.. Bajaj, MD1, Robert S.. Rahimi, MD2, Christopher Allen, MS3, Zeev Heimanson, PharmD3, Robert J.. Israel, MD3, Kris V.. Kowdley, MD, FACG4, 9, Rifaximin Monotherapy Is More Effective Than Lactulose Monotherapy for Reducing the Risk of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy (OHE) Recurrence and All-Cause Mortality: An Analysis of Two Randomized Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Jasmohan S.. Bajaj, MD1, Robert S.. Rahimi, MD2, Christopher Allen, MS3, Zeev Heimanson, PharmD3, Robert J.. Israel, MD3, Kris V.. Kowdley, MD, FACG4
1Virginia Commonwealth University and Central Virginia Veterans Healthcare System, Richmond, VA; 2Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 3Salix Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ; 4Liver Institute Northwest, Seattle, WA
Introduction: Lactulose (LAC) monotherapy (MT) is recommended as secondary prophylaxis after the first instance of OHE, with LAC plus rifaximin prescribed should additional OHE events occur. However, LAC nonadherence, which can precipitate OHE recurrence, indicates that alternative, non-LAC–based strategies are needed. The aim was to evaluate the efficacy/safety of LAC MT vs rifaximin MT.
Methods: Data were analyzed post hoc from 2 randomized trials (phase 3 double-blind; phase 4 open-label) of adults with cirrhosis and a history of OHE during the previous 6 months (currently in remission [Conn score ≤1]). Only patients who treated with rifaximin 550 mg twice daily (ie, no LAC [phase 3 or 4 trials]) or LAC (titrated to 2-3 soft stools/d) plus placebo (ie, LAC MT [phase 3 trial]) were included in the analysis. The primary efficacy endpoint was time to first breakthrough OHE episode (Conn score ≥2; original endpoint in both trials).
Results: 125 patients received rifaximin and 145 patients received LAC. The majority of patients (rifaximin; LAC) were male (60.0%; 68.3%), the mean age was about 57 y (58.2 y; 56.6 y), the median MELD score was 12 in both groups, and about half (51.2%; 46.2%) were Child-Pugh class B. A significantly smaller percentage of patients treated with rifaximin MT had an OHE episode vs those treated with LAC MT (23.2% vs 49.0%, respectively; P< 0.0001). Rifaximin MT reduced the risk of a breakthrough OHE episode by 60% vs LAC MT during 6 months of treatment, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 4 (Figure). There was a lower mortality rate in rifaximin MT vs lactulose MT group (1.6% vs 4.8%; P< 0.001), with a NNT of 19 (HR, 0.048; 95% CI, 0.01-0.29). Through follow-up (14±2 days posttreatment), mortality was reported for 2 (1.6%) patients in rifaximin MT and 10 (6.9%) patients in lactulose MT groups. Of patients who died during the study, 2 had baseline C-P class A (LAC group), 9 class B (rifaximin [n=2]; LAC [n=7]), and 1 class C (LAC group); only 2 patients (1 in each group) had a baseline MELD score of 19 or more. More LAC-treated vs rifaximin-treated patients discontinued early from study (62.1% vs 36.0%), most commonly due to HE recurrence. Rifaximin MT was well tolerated (Table).
Discussion: Significantly fewer OHE recurrence episodes were reported with rifaximin MT compared with LAC MT in patients with a history of OHE. In addition, rifaximin treatment may confer a survival benefit. Rifaximin MT may be an appropriate management approach in select patient populations.

Figure: Figure. Time to First Breakthrough OHE Episode
OHE = overt hepatic encephalopathy.
OHE = overt hepatic encephalopathy.

Table: Table. Most Common Adverse Events*
*Ranked by the highest incidence in the overall population (≥6.7%), then alphabetically (excluding hepatic encephalopathy).
*Ranked by the highest incidence in the overall population (≥6.7%), then alphabetically (excluding hepatic encephalopathy).
Disclosures:
Jasmohan Bajaj: Salix Pharmaceuticals – Clinical Trial Investigator.
Robert Rahimi: Salix Pharmaceuticals – Clinical Trial Investigator.
Christopher Allen: Salix Pharmaceuticals or its affiliates – Employee.
Zeev Heimanson: Salix Pharmaceuticals or its affiliates – Employee.
Robert Israel: Salix Pharmaceuticals or its affiliates – Employee.
Kris Kowdley: 89bio – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. CymaBay, a Gilead Sciences Company – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Enanta – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Genfit – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Gilead Sciences, Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Hanmi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. HighTide – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Intercept – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ipsen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Madrigal – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. NGM – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TERNS – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Viking – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Jasmohan S.. Bajaj, MD1, Robert S.. Rahimi, MD2, Christopher Allen, MS3, Zeev Heimanson, PharmD3, Robert J.. Israel, MD3, Kris V.. Kowdley, MD, FACG4, 9, Rifaximin Monotherapy Is More Effective Than Lactulose Monotherapy for Reducing the Risk of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy (OHE) Recurrence and All-Cause Mortality: An Analysis of Two Randomized Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.




