Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 2B - Colon / General Endoscopy / GI Bleed / Practice Management
29 - Infliximab Versus Vedolizumab in Outpatient Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
8:40 AM - 8:50 AM ET
Location: Terrace Ballroom 2-3

Matthew J. Townsend, MD, MSc
Duke University Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Joel A.. Joseph, MBBS1, Matthew J. Townsend, MD, MSc2, Aakash K. Somappa, MBBS3, Jordan Sack, MD, MPH4, Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH5, Elad Sharon, MD, MPH6, Shilpa Grover, MBBS, MPH4
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 2Duke University Medical Center, Boston, MA; 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 4Brigham and Women's Hospital / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 5Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 6Dana-Farber Cancer Institute / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) colitis is a common adverse event from cancer immunotherapy. While steroids remain first-line therapy, biologic therapy with infliximab or vedolizumab have been associated with favorable colitis outcomes in moderate-severe (CTCAE Grade ≥2) colitis. Limited retrospective studies have compared infliximab (IFX) and vedolizumab (VDZ) but across heterogeneous inpatient and outpatient cohorts. We characterized clinical effectiveness, steroid use, complication rates, and cancer outcomes following treatment with these two biologics for ICI colitis.
Methods: We retrospectively queried all adult cancer patients at our institution who received ≥1 dose of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)/ PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) inhibitor, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor, or both between January 2011 and August 2023 and received ≥1 dose of IFX or VDZ as an outpatient during this timeframe. Two independent physicians including an expert in gastrointestinal irAEs confirmed cases of biopsy-proven ICI colitis. Patients who received prior infliximab or vedolizumab for ICI colitis or for another indication (e.g. IBD), or received their first dose while hospitalized, were excluded. Complications evaluated included infections and hospitalization for colitis.
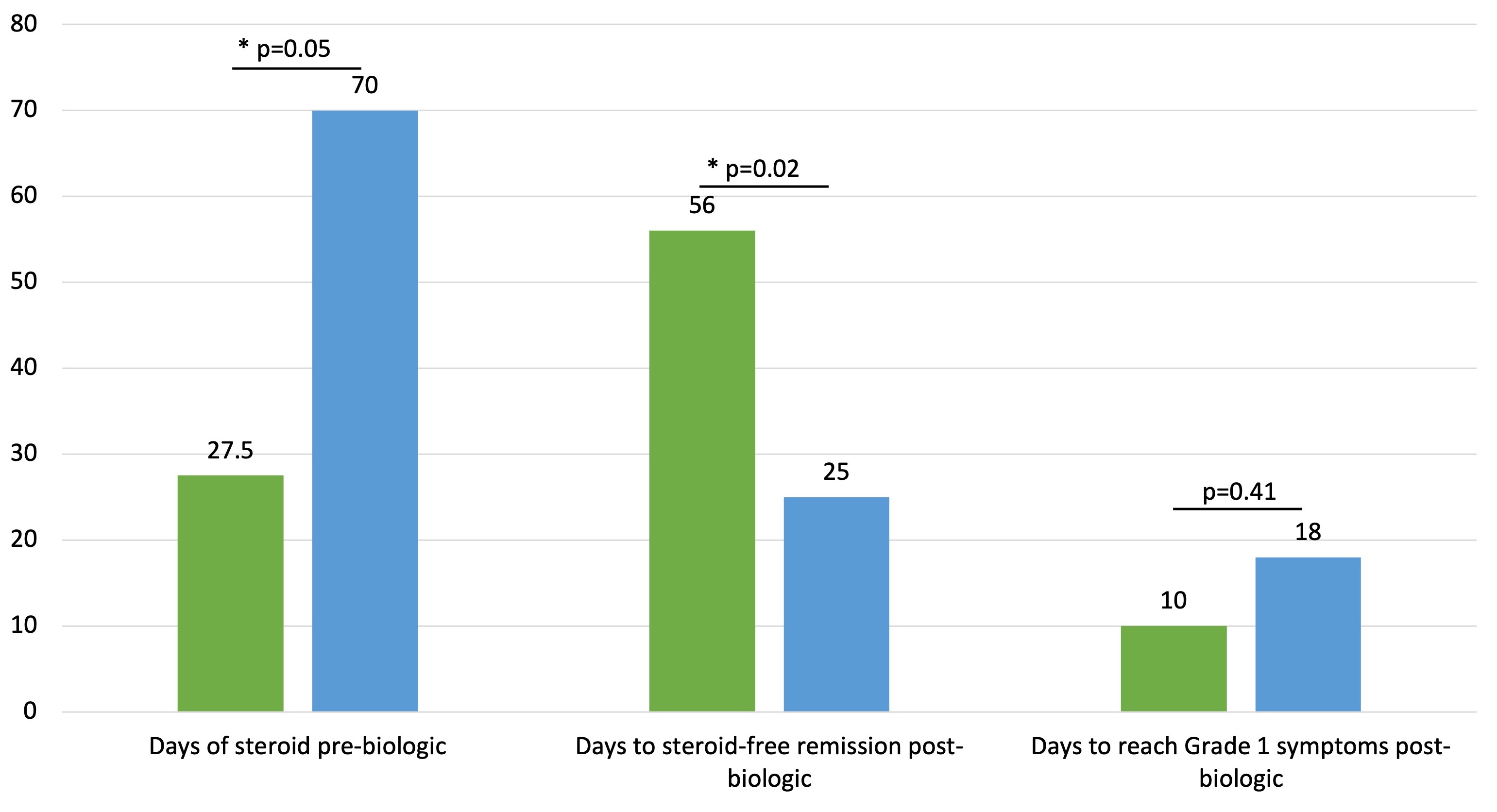
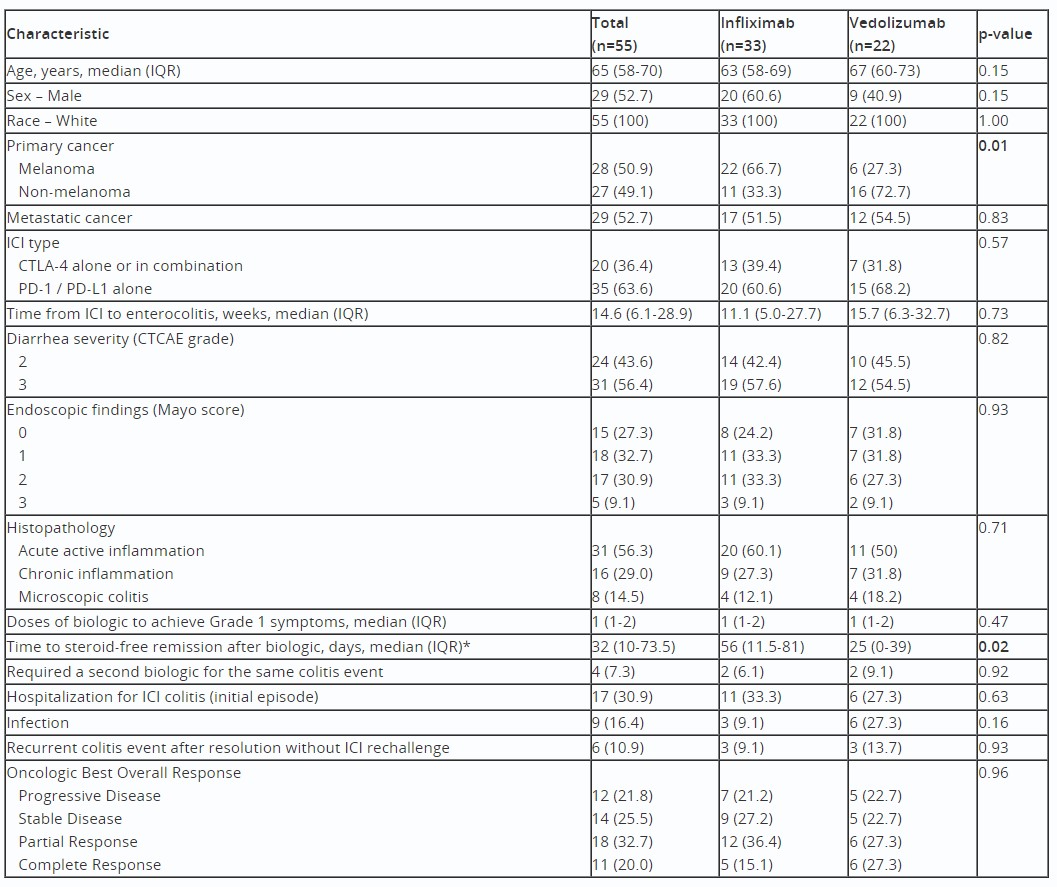
Results: A total of 55 patients treated as outpatients with IFX (n=33) or VDZ (n=22) for ICI colitis were included. Sustained clinical response (without recurrent colitis episode) was experienced in 30/33 (91%) treated with IFX and 19/22 (86%) treated with VDZ. Symptom improvement to CTCAE Grade 1 was achieved in median 10 days from IFX initiation versus 18 days for VDZ (p=0.41). Similar proportions required more than 3 total doses of biologic (24% IFX vs 27% VDZ). After biologic initiation, steroids were more rapidly discontinued in those treated with VDZ (median 25 days, IQR 0-39 days) than IFX (median 56 days, IQR 11.5-81 days) (p=0.02). A total of 17 patients (30.9%) required hospitalization for this colitis episode and 9 patients (16.4%) experienced infection; differences were not significant across treatment groups. There was no difference in oncologic best overall response across groups.
Discussion: Infliximab and vedolizumab achieved similarly high response rates among those initiated as outpatients. Shorter time to steroid-free remission with vedolizumab versus infliximab warrants confirmation in prospective clinical trials.
Disclosures:
Joel A.. Joseph, MBBS1, Matthew J. Townsend, MD, MSc2, Aakash K. Somappa, MBBS3, Jordan Sack, MD, MPH4, Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH5, Elad Sharon, MD, MPH6, Shilpa Grover, MBBS, MPH4, 29, Infliximab Versus Vedolizumab in Outpatient Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 2Duke University Medical Center, Boston, MA; 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 4Brigham and Women's Hospital / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 5Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 6Dana-Farber Cancer Institute / Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) colitis is a common adverse event from cancer immunotherapy. While steroids remain first-line therapy, biologic therapy with infliximab or vedolizumab have been associated with favorable colitis outcomes in moderate-severe (CTCAE Grade ≥2) colitis. Limited retrospective studies have compared infliximab (IFX) and vedolizumab (VDZ) but across heterogeneous inpatient and outpatient cohorts. We characterized clinical effectiveness, steroid use, complication rates, and cancer outcomes following treatment with these two biologics for ICI colitis.
Methods: We retrospectively queried all adult cancer patients at our institution who received ≥1 dose of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)/ PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) inhibitor, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor, or both between January 2011 and August 2023 and received ≥1 dose of IFX or VDZ as an outpatient during this timeframe. Two independent physicians including an expert in gastrointestinal irAEs confirmed cases of biopsy-proven ICI colitis. Patients who received prior infliximab or vedolizumab for ICI colitis or for another indication (e.g. IBD), or received their first dose while hospitalized, were excluded. Complications evaluated included infections and hospitalization for colitis.
Results: A total of 55 patients treated as outpatients with IFX (n=33) or VDZ (n=22) for ICI colitis were included. Sustained clinical response (without recurrent colitis episode) was experienced in 30/33 (91%) treated with IFX and 19/22 (86%) treated with VDZ. Symptom improvement to CTCAE Grade 1 was achieved in median 10 days from IFX initiation versus 18 days for VDZ (p=0.41). Similar proportions required more than 3 total doses of biologic (24% IFX vs 27% VDZ). After biologic initiation, steroids were more rapidly discontinued in those treated with VDZ (median 25 days, IQR 0-39 days) than IFX (median 56 days, IQR 11.5-81 days) (p=0.02). A total of 17 patients (30.9%) required hospitalization for this colitis episode and 9 patients (16.4%) experienced infection; differences were not significant across treatment groups. There was no difference in oncologic best overall response across groups.
Discussion: Infliximab and vedolizumab achieved similarly high response rates among those initiated as outpatients. Shorter time to steroid-free remission with vedolizumab versus infliximab warrants confirmation in prospective clinical trials.

Figure: Steroid Requirements and Time to Clinical Response in Outpatients Treated with Infliximab or Vedolizumab for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis. Legend: Infliximab (green bars), Vedolizumab (blue bars).

Table: Clinical Characteristics of Outpatients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) Colitis Treated with Biologic Therapy. Abbreviations: CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; IQR: interquartile range; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed cell death-1 ligand-1. *Excludes n=4 patients not treated with steroids (n=3 infliximab, n=1 vedolizumab).
Disclosures:
Joel Joseph indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Townsend indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aakash Somappa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Sack indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicole LeBoeuf: Bayer – Consultant. Fortress Biotech – Consultant. Silverback – Consultant. Synox Therapeutics – Consultant.
Elad Sharon: D. E. Shaw – Consultant. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Shilpa Grover indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel A.. Joseph, MBBS1, Matthew J. Townsend, MD, MSc2, Aakash K. Somappa, MBBS3, Jordan Sack, MD, MPH4, Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH5, Elad Sharon, MD, MPH6, Shilpa Grover, MBBS, MPH4, 29, Infliximab Versus Vedolizumab in Outpatient Treatment of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.



