Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 3B - Obesity / Biliary-Pancreas
53 - Development and Validation of a Mortality Risk Score for Acute Pancreatitis Patients in the ICU
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
3:25 PM - 3:35 PM ET
Location: Terrace Ballroom 2-3

Hassam Ali, MD
East Carolina University Brody School of Medicine
Greenville, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Auxiliary Award (Trainee)
Hassam Ali, MD1, Vishali Moond, MD2, Fnu vikash, MD3, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Waqas Rasheed, MD6, Amir Sohail, MD7, Umar Hayat, MD8, Mona A.. Ali, MD9, Pratik Patel, MD10, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS11, Fouad Jaber, MD12, Douglas Adler, MD13
1East Carolina University Brody School of Medicine, Greenville, NC; 2Saint Peter's University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ; 3Saint Peter's University Hospital/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 4The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 7NYU Langone Health, Long Island, NY; 8Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 9Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 10Mather Hospital/Hofstra University Zucker School of Medicine, Port Jefferson, NY; 11Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 12University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 13Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: Predicting inpatient mortality for acute pancreatitis (AP) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies. This study aims to develop a concise and accurate risk score model to predict 7-day and 30-day mortality in AP patients in ICU settings.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from 382 AP patients admitted to the ICU. Twenty-eight variables were initially considered and reduced using LASSO regression, followed by backward elimination in multivariate models. The final model included four key predictors: INR, albumin, creatinine, and lactic acid. The model's predictive performance was evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation, yielding mean AUC values for both 7-day and 30-day mortality.
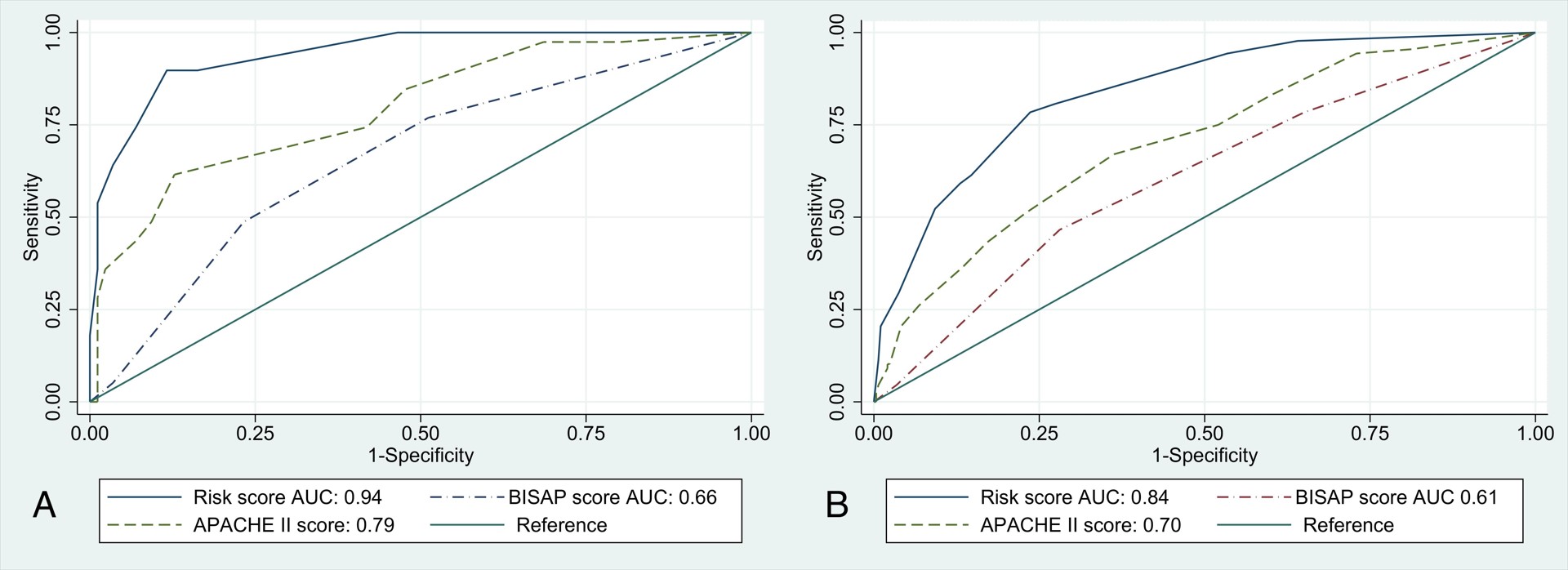
Results: The overall mortality rate was 23.2% (n=88). The LASSO regression identified 13 significant predictors, which were further refined to four key predictors in the final model. The model demonstrated a mean AUC of 0.93 (SD: 0.045) for 7-day mortality and 0.83 (SD: 0.052) for 30-day mortality. At the 7-day mark, the model exhibited a sensitivity of 78.4% and a specificity of 76.4%. For 30-day mortality, sensitivity and specificity were similarly robust. Compared to the BISAP and APACHE-II scores, our model showed superior predictive performance, with AUCs of 0.94 and 0.85 for 7-day and 30-day mortality, respectively, versus 0.66 and 0.62 for BISAP, and 0.79 and 0.71 for APACHE-II (Figure 1). High-risk patients, identified by our model, had significantly higher mortality rates, underscoring the model’s clinical utility in early identification of high-risk AP patients for timely interventions.
Discussion: Our risk score model, based on routinely available laboratory parameters, provides a reliable tool for predicting mortality in AP patients admitted to the ICU. It offers a significant improvement over current scoring systems, facilitating better resource allocation and timely interventions.
Disclosures:
Hassam Ali, MD1, Vishali Moond, MD2, Fnu vikash, MD3, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Waqas Rasheed, MD6, Amir Sohail, MD7, Umar Hayat, MD8, Mona A.. Ali, MD9, Pratik Patel, MD10, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS11, Fouad Jaber, MD12, Douglas Adler, MD13, 53, Development and Validation of a Mortality Risk Score for Acute Pancreatitis Patients in the ICU, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Hassam Ali, MD1, Vishali Moond, MD2, Fnu vikash, MD3, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Waqas Rasheed, MD6, Amir Sohail, MD7, Umar Hayat, MD8, Mona A.. Ali, MD9, Pratik Patel, MD10, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS11, Fouad Jaber, MD12, Douglas Adler, MD13
1East Carolina University Brody School of Medicine, Greenville, NC; 2Saint Peter's University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ; 3Saint Peter's University Hospital/Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 4The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 7NYU Langone Health, Long Island, NY; 8Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 9Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 10Mather Hospital/Hofstra University Zucker School of Medicine, Port Jefferson, NY; 11Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 12University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 13Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: Predicting inpatient mortality for acute pancreatitis (AP) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies. This study aims to develop a concise and accurate risk score model to predict 7-day and 30-day mortality in AP patients in ICU settings.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from 382 AP patients admitted to the ICU. Twenty-eight variables were initially considered and reduced using LASSO regression, followed by backward elimination in multivariate models. The final model included four key predictors: INR, albumin, creatinine, and lactic acid. The model's predictive performance was evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation, yielding mean AUC values for both 7-day and 30-day mortality.
Results: The overall mortality rate was 23.2% (n=88). The LASSO regression identified 13 significant predictors, which were further refined to four key predictors in the final model. The model demonstrated a mean AUC of 0.93 (SD: 0.045) for 7-day mortality and 0.83 (SD: 0.052) for 30-day mortality. At the 7-day mark, the model exhibited a sensitivity of 78.4% and a specificity of 76.4%. For 30-day mortality, sensitivity and specificity were similarly robust. Compared to the BISAP and APACHE-II scores, our model showed superior predictive performance, with AUCs of 0.94 and 0.85 for 7-day and 30-day mortality, respectively, versus 0.66 and 0.62 for BISAP, and 0.79 and 0.71 for APACHE-II (Figure 1). High-risk patients, identified by our model, had significantly higher mortality rates, underscoring the model’s clinical utility in early identification of high-risk AP patients for timely interventions.
Discussion: Our risk score model, based on routinely available laboratory parameters, provides a reliable tool for predicting mortality in AP patients admitted to the ICU. It offers a significant improvement over current scoring systems, facilitating better resource allocation and timely interventions.

Figure: Figure 1. Comparison of the Performance of Risk Score Compared to BISAP score and APACHE II score in Predicting 7-day and 30-day Mortality

Table: Table 1. Baseline demographic variables before and after matching in the present study
Disclosures:
Hassam Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishali Moond indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu vikash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manesh Kumar Gangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waqas Rasheed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amir Sohail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pratik Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fouad Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Douglas Adler: Boston Scientific and Micro Tech. – Consultant.
Hassam Ali, MD1, Vishali Moond, MD2, Fnu vikash, MD3, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Waqas Rasheed, MD6, Amir Sohail, MD7, Umar Hayat, MD8, Mona A.. Ali, MD9, Pratik Patel, MD10, Syed Muhammad Ali Najafi, MBBS11, Fouad Jaber, MD12, Douglas Adler, MD13, 53, Development and Validation of a Mortality Risk Score for Acute Pancreatitis Patients in the ICU, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.



