Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4275 - Single Ascending Dose Results From a Phase 1 Clinical Trial of BT-600, a Combination Product of the NaviCap Targeted Oral Delivery Platform and Tofacitinib
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

.jpg)
Brian G. Feagan, MD
Western University
London, ON, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Ghesal Razag, BA2, Adebola C. Fabiyi, PhD2, Shaoying N. Lee, PhD3, Gregory Armaos, MSc4, Paul W. Shabram, BA, MBA5, Sharat Shingh, PhD3, Ariella Kelman, MD3
1Western University, London, ON, Canada; 2Biora Therapeutics, Inc., San Diego, CA; 3Biora Therapeutics, San Diego, CA; 4Celerion, Laval, PQ, Canada; 5Biora Therapeutics Inc., San Diego, CA
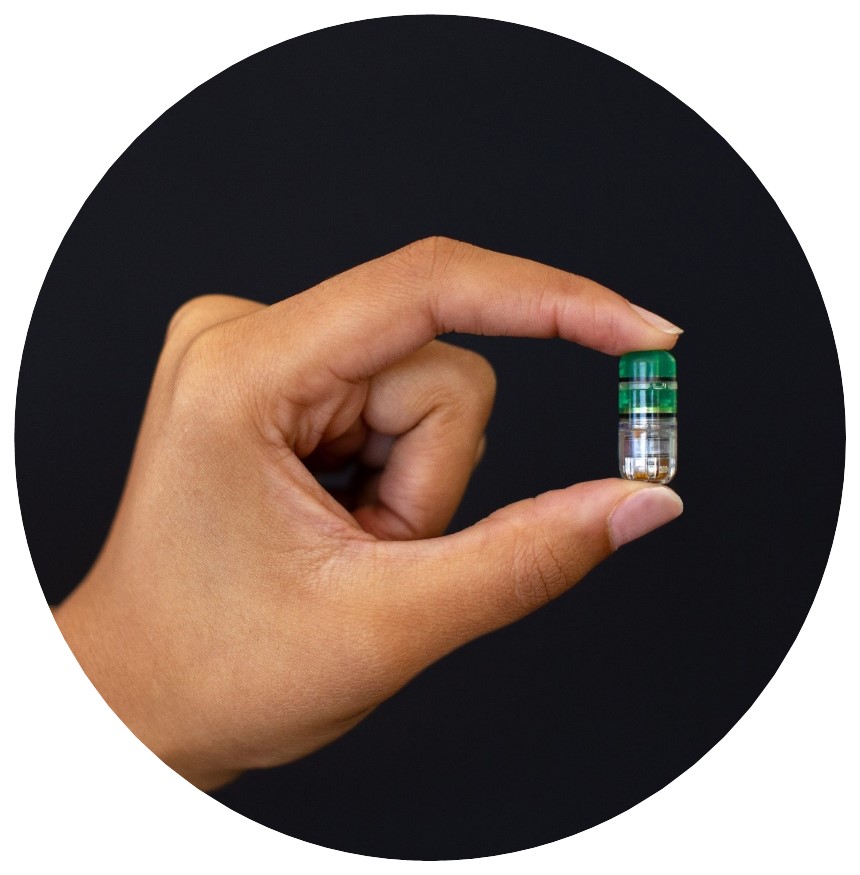
Introduction: The NaviCap platform uses an oral drug delivery capsule that autonomously identifies locations in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract for anatomically targeted delivery (Fig. 1). The device is designed to deliver a liquid drug formulation directly to the colon mucosa, bypassing the upper GI tract. In patients with ulcerative colitis, delivery to the colon could improve efficacy and reduce toxicity with lower systemic drug exposure. Results of device function studies without drug have previously been reported. Here we report interim results of the Phase 1 clinical trial of BT-600, a drug-device combination of NaviCap with a liquid formulation of tofacitinib.
Methods: This Phase 1 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single and multiple ascending dose (SAD/MAD) clinical trial evaluated the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of BT-600 in healthy adult participants. In Part 1, participants (n=24) received a single dose of BT-600 with tofacitinib 5 mg (n=9), 10 mg (n=9), or placebo (n=6). Part 2 (n=24) will assess safety, plasma, and colonic tissue exposure of BT-600 or placebo daily for 7 days. A pre-specified interim analysis included results on safety, plasma PK, and evidence of drug in feces in Part 1.
Results: Adverse events were mild, transient, and consistent with those expected in a healthy population. All 24 participants demonstrated systemic absorption following a single dose, with PK parameters consistent with colonic delivery, in distinction to delivery in the upper GI tract. Tofacitinib was first detected in plasma at ~6 hours following administration of BT-600. The median time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was 8–10 hours vs 0.5–1.0 hours for conventional oral tofacitinib. Colonic delivery of BT-600 was associated with 3–4x lower systemic absorption of tofacitinib vs conventional oral tofacitinib, with plasma tofacitinib Cmax arithmetic mean (SD) values of 26 (14.8) ng/mL for BT-600 at the 10 mg dose (Table 1). Drug was present in fecal samples of all participants. Overall AUCs and peak (Cmax) exposures to plasma tofacitinib increased in a dose proportional manner from BT-600 5 mg to 10 mg.
Discussion: Interim results of the Phase 1 clinical trial in healthy adult participants showed that BT-600 was well tolerated and achieved colonic drug delivery with lower systemic exposure than seen with conventional oral tofacitinib.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Ghesal Razag, BA2, Adebola C. Fabiyi, PhD2, Shaoying N. Lee, PhD3, Gregory Armaos, MSc4, Paul W. Shabram, BA, MBA5, Sharat Shingh, PhD3, Ariella Kelman, MD3. P4275 - Single Ascending Dose Results From a Phase 1 Clinical Trial of BT-600, a Combination Product of the NaviCap Targeted Oral Delivery Platform and Tofacitinib, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Ghesal Razag, BA2, Adebola C. Fabiyi, PhD2, Shaoying N. Lee, PhD3, Gregory Armaos, MSc4, Paul W. Shabram, BA, MBA5, Sharat Shingh, PhD3, Ariella Kelman, MD3
1Western University, London, ON, Canada; 2Biora Therapeutics, Inc., San Diego, CA; 3Biora Therapeutics, San Diego, CA; 4Celerion, Laval, PQ, Canada; 5Biora Therapeutics Inc., San Diego, CA
Introduction: The NaviCap platform uses an oral drug delivery capsule that autonomously identifies locations in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract for anatomically targeted delivery (Fig. 1). The device is designed to deliver a liquid drug formulation directly to the colon mucosa, bypassing the upper GI tract. In patients with ulcerative colitis, delivery to the colon could improve efficacy and reduce toxicity with lower systemic drug exposure. Results of device function studies without drug have previously been reported. Here we report interim results of the Phase 1 clinical trial of BT-600, a drug-device combination of NaviCap with a liquid formulation of tofacitinib.
Methods: This Phase 1 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single and multiple ascending dose (SAD/MAD) clinical trial evaluated the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of BT-600 in healthy adult participants. In Part 1, participants (n=24) received a single dose of BT-600 with tofacitinib 5 mg (n=9), 10 mg (n=9), or placebo (n=6). Part 2 (n=24) will assess safety, plasma, and colonic tissue exposure of BT-600 or placebo daily for 7 days. A pre-specified interim analysis included results on safety, plasma PK, and evidence of drug in feces in Part 1.
Results: Adverse events were mild, transient, and consistent with those expected in a healthy population. All 24 participants demonstrated systemic absorption following a single dose, with PK parameters consistent with colonic delivery, in distinction to delivery in the upper GI tract. Tofacitinib was first detected in plasma at ~6 hours following administration of BT-600. The median time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was 8–10 hours vs 0.5–1.0 hours for conventional oral tofacitinib. Colonic delivery of BT-600 was associated with 3–4x lower systemic absorption of tofacitinib vs conventional oral tofacitinib, with plasma tofacitinib Cmax arithmetic mean (SD) values of 26 (14.8) ng/mL for BT-600 at the 10 mg dose (Table 1). Drug was present in fecal samples of all participants. Overall AUCs and peak (Cmax) exposures to plasma tofacitinib increased in a dose proportional manner from BT-600 5 mg to 10 mg.
Discussion: Interim results of the Phase 1 clinical trial in healthy adult participants showed that BT-600 was well tolerated and achieved colonic drug delivery with lower systemic exposure than seen with conventional oral tofacitinib.

Figure: Figure 1: The NaviCap Device
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Brian Feagan: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. AbolerIS – Consultant. AgomAB Therapeutics – Consultant. Allianthera – Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AnaptysBio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Applied Molecular Transport Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Arena Pharma – Consultant. Atomwise – Consultant. Avoro Capital Advisors – Consultant. Axio Research – Advisory Committee/Board Member. BioJamp – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boxer – Consultant. Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Celsius Therapeutics – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant, stock or other ownership interest. Cytoki – Consultant. Disc Medicine – Consultant. Duality – Consultant. EcoR1 Capital – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Ermium – Consultant. First Wave – Consultant. First Word Group – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Galen Atlantica – Consultant. Genentech/Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gossamer Pharma – Consultant, Stock Options. Hinge Bio – Consultant. Hot Spot Therapeutics – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Immunic Therapeutics – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAKAcademy – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Japan Tobacco Inc. – Consultant. Kaleido Biosciences – Consultant. L.E.K. Consulting – Consultant. Landos Biopharma – Consultant. Leadiant – Consultant. Lenczner Slaght – Consultant, payment for expert testimony. LifeSci Capital – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Lument AB – Consultant. Millennium – Consultant. MiroBio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Morgan Lewis – Consultant, payment for expert testimony. Morphic Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Mylan – Consultant. OM Pharma – Consultant. Origo BioPharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Orphagen – Consultant. Pandion Therapeutics – Consultant. Pendopharm – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Play to Know AG – Consultant. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Protagonist – Consultant. PTM Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rebiotix – Consultant. REDX – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Consultant. Silverback Therapeutics – Consultant. Surrozen Inc. – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Teva – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Thelium – Consultant. Tigenix – Consultant. Tillotts Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant. VHSquared Ltd – Consultant. Viatris – Consultant. Ysios – Consultant. Ysopia – Consultant. Zealand Pharma – Consultant.
Ghesal Razag: Biora Therapeutics – Employee.
Adebola Fabiyi: Biora Therapeutics – Employee.
Shaoying Lee: Biora Therapeutics – Employee.
Gregory Armaos: Celerion – Employee.
Paul Shabram: Biora Therapeutics, Inc. – Employee.
Sharat Shingh: Biora Therapeutics – Employee.
Ariella Kelman: Biora Therapeutics – Employee, Stock Options.
Brian G.. Feagan, MD1, Ghesal Razag, BA2, Adebola C. Fabiyi, PhD2, Shaoying N. Lee, PhD3, Gregory Armaos, MSc4, Paul W. Shabram, BA, MBA5, Sharat Shingh, PhD3, Ariella Kelman, MD3. P4275 - Single Ascending Dose Results From a Phase 1 Clinical Trial of BT-600, a Combination Product of the NaviCap Targeted Oral Delivery Platform and Tofacitinib, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

