Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4692 - Applying Large Language Models to Better Understand Psychosocial Factors Influencing Successful Liver Transplant Completion
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- ER
Emily Robitschek, BS
University of California San Francisco
San Francisco, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Emily Robitschek, BS, Asal Bastani, BS, Savyon Sordean, , Kathryn Horwath, JD, Jennifer Lai, MD, MBA, Mark Pletcher, MD, MPH, Irene Chen, PhD, Jin Ge, MD, MBA
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
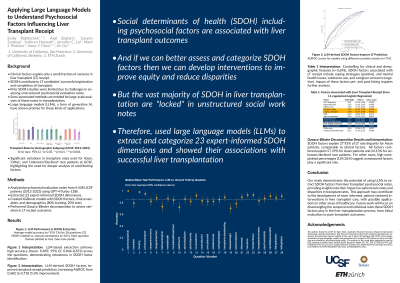
Introduction: Social determinants of health (SDOH) are significant factors contributing to liver transplant (LT) candidates’ successful LT completion. Prior studies of SDOH factors have been limited due to challenges with working with unstructured data in LT psychosocial evaluation notes.
Methods: We utilized the GPT-4-Turbo-128k large language model (LLM) to analyze LT psychosocial evaluation notes from 4,258 adult patients evaluated for LT at UCSF between 2012-2023. We used prompt engineering to systematically extract 23 SDOH factors with an overall accuracy of 0.860 (95%CI:0.84-0.88) compared to manual annotations for a random subset (n=51). Accuracies across the 23 factors ranged from 0.59 (95%CI:0.45-0.73) to 0.98 (95%CI:0.94-1.00). We combined SDOH factors with demographic/clinical factors and used L1-regularized logistic regression to associate them with the outcome of successful LT. All p-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons.
Results: Of the 4,258, 1,525 (35.8%) successfully completed LT. Among clinical and demographic factors, hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis (OR:1.68, 95%CI:1.20-2.34, p=0.014) and MELD score (OR:1.42/standard deviation increase, 95%CI:1.31-1.53, p< 0.0001) were associated with successful LT. Asian patients were more likely to receive LT (OR:1.34, 95%CI:1.06-1.69, p=0.060), whereas patients of "other" (OR:0.60, 95% CI:0.43-0.84, p=0.015) or unknown/declined race/ethnicity (OR:0.25, 95%CI:0.16-0.40, p< 0.0001) were less likely to receive LT. Non-English preferred language was also negatively associated with successful LT (OR:0.57, 95%CI:0.42-0.79, p=0.0058).
Regarding SDOH factors (excluding formal psychosocial recommendations and factors associated with the etiology of liver disease), positive associations included presence of coping skills (OR:1.68, 95%CI:1.20-2.34, p=0.014) and presence of a translator during the evaluation (OR:1.51, 95%CI:1.10-2.08, p=0.048). Negative associations included ongoing non-alcohol substance use (OR:0.74, 95%CI: 0.62-0.89, p=0.0080), concerns with the caregiver plan (OR:0.56, 95%CI:0.41-0.75, p=0.0015), and active mental health issues (OR:0.72, 95%CI:0.58-0.89, p=0.013).
Discussion: This study is one of the first to systematically extract SDOH factors from LT psychosocial evaluation notes and showed the use of advanced LLM methods to better elucidate SDOH factors important for LT. Our results indicate that ongoing non-alcohol substance use, translation services, and caregiver support could be points for intervention for LT completion.
Disclosures:
Emily Robitschek, BS, Asal Bastani, BS, Savyon Sordean, , Kathryn Horwath, JD, Jennifer Lai, MD, MBA, Mark Pletcher, MD, MPH, Irene Chen, PhD, Jin Ge, MD, MBA. P4692 - Applying Large Language Models to Better Understand Psychosocial Factors Influencing Successful Liver Transplant Completion, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Introduction: Social determinants of health (SDOH) are significant factors contributing to liver transplant (LT) candidates’ successful LT completion. Prior studies of SDOH factors have been limited due to challenges with working with unstructured data in LT psychosocial evaluation notes.
Methods: We utilized the GPT-4-Turbo-128k large language model (LLM) to analyze LT psychosocial evaluation notes from 4,258 adult patients evaluated for LT at UCSF between 2012-2023. We used prompt engineering to systematically extract 23 SDOH factors with an overall accuracy of 0.860 (95%CI:0.84-0.88) compared to manual annotations for a random subset (n=51). Accuracies across the 23 factors ranged from 0.59 (95%CI:0.45-0.73) to 0.98 (95%CI:0.94-1.00). We combined SDOH factors with demographic/clinical factors and used L1-regularized logistic regression to associate them with the outcome of successful LT. All p-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons.
Results: Of the 4,258, 1,525 (35.8%) successfully completed LT. Among clinical and demographic factors, hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis (OR:1.68, 95%CI:1.20-2.34, p=0.014) and MELD score (OR:1.42/standard deviation increase, 95%CI:1.31-1.53, p< 0.0001) were associated with successful LT. Asian patients were more likely to receive LT (OR:1.34, 95%CI:1.06-1.69, p=0.060), whereas patients of "other" (OR:0.60, 95% CI:0.43-0.84, p=0.015) or unknown/declined race/ethnicity (OR:0.25, 95%CI:0.16-0.40, p< 0.0001) were less likely to receive LT. Non-English preferred language was also negatively associated with successful LT (OR:0.57, 95%CI:0.42-0.79, p=0.0058).
Regarding SDOH factors (excluding formal psychosocial recommendations and factors associated with the etiology of liver disease), positive associations included presence of coping skills (OR:1.68, 95%CI:1.20-2.34, p=0.014) and presence of a translator during the evaluation (OR:1.51, 95%CI:1.10-2.08, p=0.048). Negative associations included ongoing non-alcohol substance use (OR:0.74, 95%CI: 0.62-0.89, p=0.0080), concerns with the caregiver plan (OR:0.56, 95%CI:0.41-0.75, p=0.0015), and active mental health issues (OR:0.72, 95%CI:0.58-0.89, p=0.013).
Discussion: This study is one of the first to systematically extract SDOH factors from LT psychosocial evaluation notes and showed the use of advanced LLM methods to better elucidate SDOH factors important for LT. Our results indicate that ongoing non-alcohol substance use, translation services, and caregiver support could be points for intervention for LT completion.
Disclosures:
Emily Robitschek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asal Bastani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Savyon Sordean indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathryn Horwath indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer Lai: Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Genfit – Consultant. Lipocene – Grant/Research Support. Nestle Nutrition Sciences – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Third Rock Ventures – Consultant. Vir Biotechnologies – Grant/Research Support.
Mark Pletcher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irene Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jin Ge: Astellas Pharmaceuticals/Iota Biosciences – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Madrigal Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Merck and Co – Grant/Research Support.
Emily Robitschek, BS, Asal Bastani, BS, Savyon Sordean, , Kathryn Horwath, JD, Jennifer Lai, MD, MBA, Mark Pletcher, MD, MPH, Irene Chen, PhD, Jin Ge, MD, MBA. P4692 - Applying Large Language Models to Better Understand Psychosocial Factors Influencing Successful Liver Transplant Completion, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
